Thioamide-stabilized peptide specifically inhibiting cathepsin L to block SARS-CoV-2 entry and cancer cell migration
Problem:
Cathepsin L is a protease which is upregulated in many cancers such as breast cancer, colorectal cancer, and pancreatic adenocarcinoma. The enzyme cleaves cell membrane components, destabilizing adhesion, and promotes invasion and metastasis. Recently, Cathepsin L was also found to be important for SARS-CoV-2 entry into host cells during infection. Despite its role in various diseases, there are no specific Cathepsin L inhibitors in clinical trials, because small-molecule drugs also inhibit closely related cathepsins including V, K, S, and B, triggering off-target effects.
Solution:
Compared to small-molecule, peptide-based drugs offer higher selectivity and binding affinities towards their targets. These characteristics mitigate unwanted side-effects and improves therapeutic efficacy at lower drug doses. The invention is a peptide which binds to and inhibits Cathepsin L but interacts weakly with related cathepsins. Additionally, because peptides are prone to rapid degradation in the body, a modification in the peptide backbone prevents proteolysis, increasing its stability and half-life. The peptide inhibitor may potentially be applied to treat different cancers and SARS-CoV-2.
Technology:
The Cathepsin L peptide inhibitor, RS1A, is designed with a thioamide substitution at the P1 proteolytic position. This single atom O-to-S exchange in the peptide backbone stabilizes the molecule against proteolysis by all five cathepsins (L, V, K, S, B) without decreasing inhibitory activity against Cathepsin L. To increase specificity towards Cathepsin L, a basic residue was chosen for the P1 position, and histidine was used at the P4 position.
Advantages:
- Greater than 25-fold specific Cathepsin L inhibitor over Cathepsins V, S, K, B
- Low micromolar inhibition of Cathepsin L
- No degradation after 6 hours of incubation with whole cell lysate
- Half-life of ~24 hours in whole cell lysate
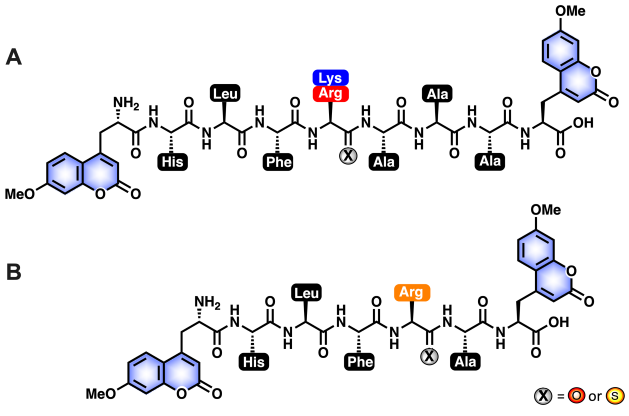
Figure caption: All-amide Peptides and Thioamide Peptides Investigated in this Study. (A) Sequence[1]optimized all-amide and thioamide peptides of K3A (µHLFKAAAµ) and R3A (µHLFRAAAµ) for initial steady-state protease scanning with Cts L, Cts V, Cts K, Cts S, and Cts B and inhibition studies with Cts L. The peptides contain 7-methoxycoumarin-4-yl-alanine (MCM; µ) residues at both termini, and either an amide (X=O) or a thioamide (X=S) residue at the denoted P1 position. (B) Truncated all-amide and thioamide R1A peptide (µHLFRAµ). The RS1A peptide, which shows stabilization against all five proteases, was further investigated for specificity and inhibitory effect in HepG2 whole cell lysate. Figure taken from Figure 1 in preprint: Phan et al. "Rational Design of Thioamide Peptides as Selective Inhibitors of Cysteine Protease Cathepsin L" - Chemical Science (RSC Publishing) DOI: 10.1039/D1SC00785H
Desired Partnerships:
- License
- Co-development (this replaces collaboration or sponsored research)