New fabrication techniques for CdSe QD FETs
Problem:
Many researchers are attempting to create flexible electronics, which could have applications for new mobile and wearable devices. However, traditional semiconductor materials are not flexible, so new materials and fabrication techniques are needed to make flexible electronics possible.
Solution:
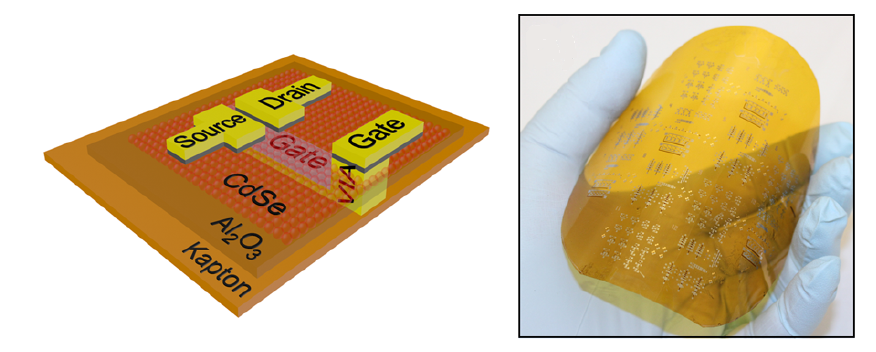
Researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have created flexible electronic materials based on CdSe quantum dot (QD) thin-film field effect transistors (FETs). A new processing technique enables low-cost, wide-area fabrication of QD thin films in a process compatible with plastic substrates. An additional doping step makes these devices stable when exposed to air. This makes air-exposed fabrication techniques such as photolithography and atomic layer deposition possible.
The fabrication technique developed at Penn has been used to create QD FET based transistors, invertors, amplifiers, NOR & NAND gates, and ring oscillators. Electron mobility for these materials has been demonstrated from 13-22 cm^2/Vs, orders of magnitude higher than previous QD FET efforts, producing results comparable or superior to silicon FETs.
Advantages:
Case ID:
Y6232-tpNCS
Web Published:
3/10/2021
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |