A scalable, parallelized, multi-channel microfluidic device for generating lipid nanoparticles.
Problem:
Lipid nanoparticles are a promising delivery technology for RNA therapeutics and vaccines. However, there is a lack of formulation strategies that can produce nanoparticles with precisely defined properties that have scalable throughputs ranging from early development to clinical translation. Prior microfluidic technologies have been used to produce lipid nanoparticles with high potency and desirable physical properties, but are limited by their ability to scale to throughputs relevant for clinical studies.
Solution:
A scalable, parallelized microfluidic device (PMD) that incorporates an architecture that allows for large-scale production of lipid nanoparticles and achieves >100x production rates compared to microfluidic small scale (single channel) lipid nanoparticle formulation strategies.
Technology Overview:
The PMD incorporates an array of 128 mixing channels for large scale production of lipid nanoparticles with a single set of inlets and outlet. The PMD is composed of polydimethylsiloxane/glass and is fabricated using double-sided imprinting. The device consists of lithographically defined filters at each inlet designed to avoid channel clogging. It includes a ladder geometry with small channels that increases fluidic resistance to ensure that each mixing channel in the array produces lipid nanoparticles with identical physical parameters.
Advantages:
- >100x production rates compared to single microfluidic channels.
- Generate large scale lipid nanoparticles while maintaining physical properties and potency typical of microfluidic-formulated lipid nanoparticles
- Scalable throughput from drug discovery to clinical manufacturing
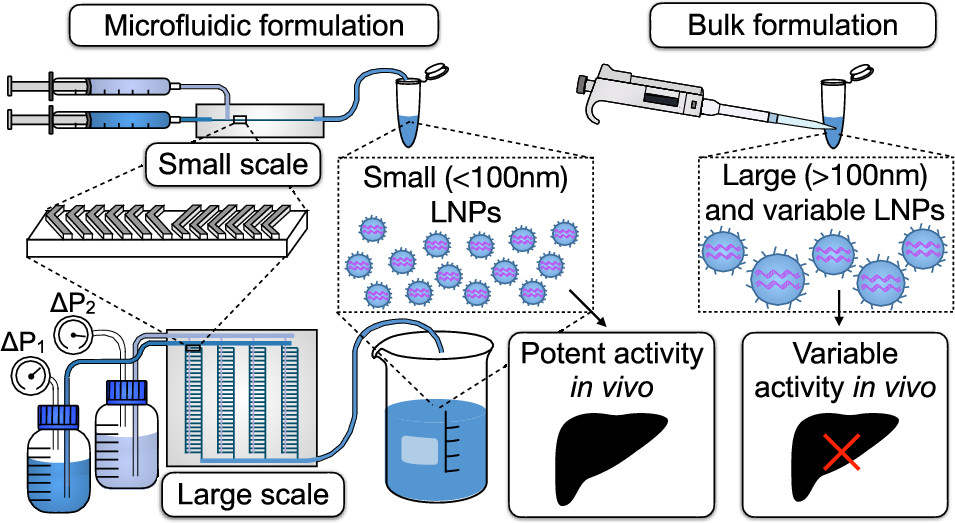
Fabrication of a scalable PDMS-based microfluidic platform for precise and large-scale RNA lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations. Microfluidic formulation produces smaller and more homogeneous LNPs for potent RNA delivery, while larger and more heterogeneous LNPs produced by bulk methods are more variable in terms of RNA delivery. Microfluidic formulation can be scaled up using the same design (staggered herringbone micromixers) for rapid mixing to produce comparable LNPs for RNA delivery.
Case ID:
21-9566-tpNCS
Web Published:
10/9/2021
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |