A machine learning classification algorithm that incorporates several smaller algorithms trained on specific tasks and selectively focuses on synergistic tasks to reduce data requirements while increasing accuracy.
Problem:
There is a need in the field of machine learning to reduce the amount of data required to train models for diverse tasks. For example, image processing algorithms are important for self-driving cars, which need to be trained on many different types of images. In addition, in certain models some tasks conflict with one another resulting in less accuracy due to the competition among the dissonant tasks.
Solution:
Model Zoo is a boosting-based algorithm built on many smaller algorithms. As a result of this method, higher accuracy is obtained as compared to the accuracy obtained when multiple data sets are fitted to one algorithm. Furthermore, this method requires less data for training and allows for training on tasks whose accuracy may compete with other tasks, without compromising accuracy.
Technology:
The inventors utilize multiple models together in a way that increases the power of the whole system without compromising the accuracy of each independent model. The resulting algorithm combines many small models trained on specific tasks. It selectively uses relevant tasks while filtering out tasks where there is a negative or no statistical benefit to their inclusion.
Advantages:
- Thoroughly tested on image classification benchmarks
- Improved accuracy over state of the art algorithms
- Outperforms five tested algorithms
- Decreased training cost for large datasets
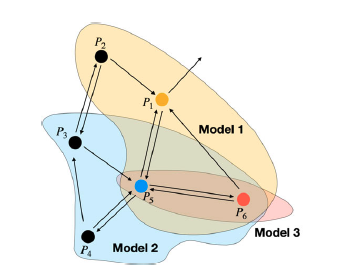
Figure shows the training of similar tasks together, for example, training Model 1 for P1 using learning from P2, P5, and P6. Ultimately, all models that were trained on a particular task would be used to make predictions. For example, in the case of P5, Models 1, 2, and 3 would be used. (P refers to a task.)
Case ID:
22-9818-tpNCS
Web Published:
5/12/2023
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |