The deep learning algorithm retrospectively improves the resolution of routine medical images (e.g., CT, MRI, etc.) without the need for increased radiation or scan time.
Technology:
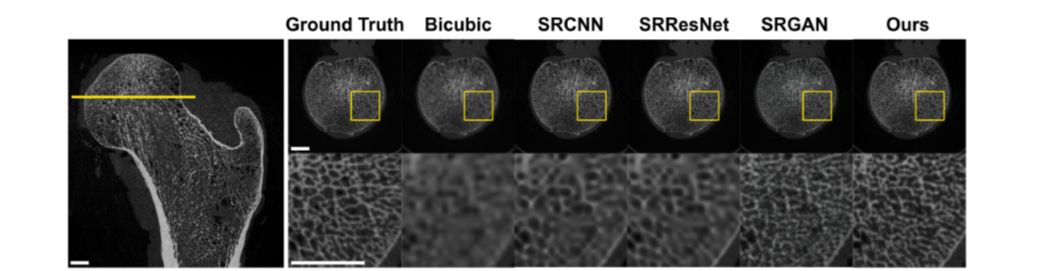
Clinical medical images often have low resolution due to radiation-dose or scan-time restrictions. Inventors developed a probabilistic deep learning model to improve resolution of routinely acquired medical images. The method is particularly suited for situations where high resolution imaging using MRI, CT, or PET is not clinically feasible. This method produces significantly better performance in terms of superior image quality, greater quantitative-measurement accuracy, and low bias compared to other methods using convolutional neural networks and generative adversarial networks (GAN). For example, this method allows the measurement of microstructural trabecular bone thickness, separation, number, and strength which can assist in evaluating bone health without the need for a bone biopsy.
Advantages:
- Improved resolution of routine low resolution clinical images
- Saving MR scan time
- Reducing radiation dose for CT scanning
- Providing information on bone health at a low radiation dose
- Opportunistic scanning for osteoporosis using low dose CT scans
- Improved performance compared to other super-resolution methods
Stage of Development:
- Validated using 60,000 CT images from cadaveric human bone for CT and hundreds of MRI images from human subjects for MRI.
Case ID:
22-9999-tpNCS
Web Published:
5/12/2023
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |