A library of bi-phosphonate ionizable lipids and LNP formulations to facilitate mRNA delivery to the bone microenvironment.
Problem:
The increasing prevalence of skeletal diseases such as osteoporosis, osteoarthritis and bone cancer have motivated efforts to target the bone microenvironment therapeutically. However, therapeutic agents must overcome multiple challenges in order to reach the key compartments of bone including reduced blood flow compared to highly vascularized tissue, poor penetration of the blood-bone marrow barrier, insufficient perfusion of bone, and low chemical affinity for bone mineral.
Solution:
Biphoshphonate (BP) lipid-like materials improve the ability of LNPs to deliver encapsulated mRNAs to the bone microenviroment. Enhanced protein expression is observed in leg bone after in-vivo injection, and within cells of both the myeloid and lymphoid lineages arising from the bone marrow compartment.
Technology:
BP lipid-like materials incorporated into lipid nanoparticle (LNP) formulations interact strongly with hydroxyapatite, a key inorganic component of bone. Using a single biphosphonate compound as a core scaffold, the inventors derive 21 unique compounds and test their ability to facilitate mRNA and protein expression in-vitro and in-vivo compared to LNPs with no biphosphonates in their formulation.
Advantages:
- 21 BP-lipid like LNP variations with a lead formulation identified
- Increases mRNA delivery in bone and in the bone marrow cells including T cells, B cells and monocytes
- Enhanced mRNA encoded protein production on bone surface and in bone marrow
- BP lipid-like containing LNPs can encapsulate diverse therapeutic approaches enhancing or silencing protein expression
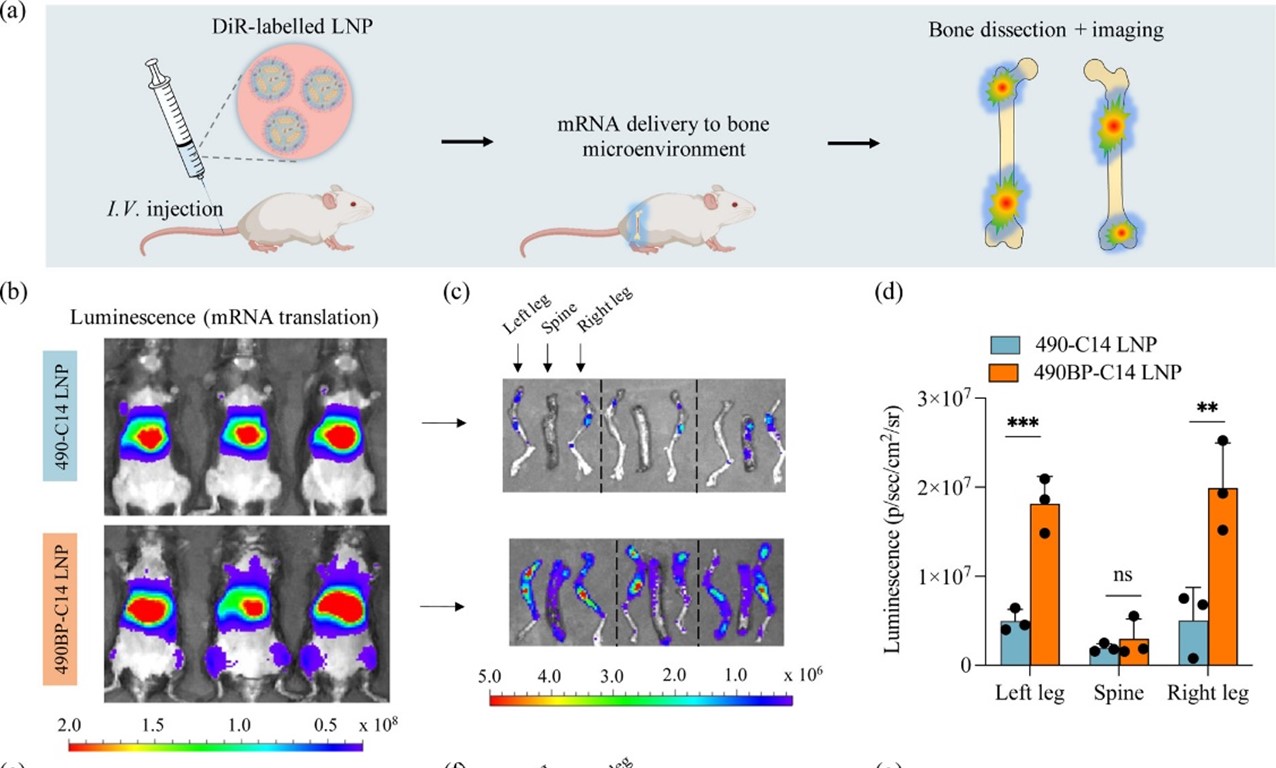
Figure caption: a) LNPs fluorescently labeled with near infrared dye (DiR) track mRNA delivery to bone. b-d) Elevated fluorescence within left and right mouse leg bone is detectable after injection of biphosphonate lipid-like formulations (490BP-C14) compared to standard LNPs (490-C14).
Stage of Development:
- Therapeutics
- Target Identified
- Preclinical Discovery
Case ID:
22-9991-tpNCS
Web Published:
5/12/2023
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |