Innovative CT contrast agent using biodegradable polymer-encapsulated gold nanoparticles for enhanced imaging and safe excretion.
Problem:
Gold particles emerged as promising contrasting agents due to their high X-ray attenuation, but their size-dependent behavior posed a challenge. Particles larger than 5nm raised toxicity concerns due to potential accumulation in the body, whereas particles smaller than 5nm were excreted too quickly to be useful.
Solution:
The inventors introduce a novel CT contrast agent, utilizing biodegradable polymer encapsulated gold nanoparticles and optimizing particle size for superior imaging quality while ensuring safe and complete excretion post-imaging.
Technology:
Leveraging the biocompatibility and degradation properties of polymers such as polyphosphazene, the inventors encapsulated gold particles, creating a stable and effective contrast agent. The encapsulation ensures that smaller gold particles remain in the bloodstream long enough for imaging, then degrades to release the particles for safe excretion.
Advantages:
- Gold nanoparticles provide superior contrast in CT images compared to iodinated agents, facilitating better diagnostics and patient care.
- Can be given to patients for whom iodinated agents are contraindicated (i.e. patients with type 2 diabetes).
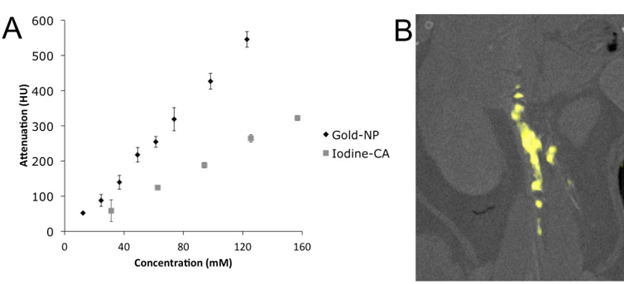
A) Attenuation of gold nanoparticles (Gold-NP) compared to iodine (Iodine-CA). B) Spectral CT image of gold nanoparticles accumulated in the aorta of an atherosclerotic mouse.
Stage of Development:
- Proof of concept in vivo mouse model
Case ID:
z6642-TpNCS
Web Published:
11/7/2023
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |