Nuclear speckles marker predicts cancer patients survival as well as response to therapy, particularly HIF2α inhibitors.
Technology:
Nuclear speckles are membrane-less bodies within the cell nucleus enriched in RNA biogenesis, processing, and export factors. Inventors at the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine demonstrated that RNA-based speckle signature is evident in 24 different cancer types and can be used as a predictor of cancer patient survival in 6 cancer types. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) showed the particularly prominent correlation and is known to be associated with hyperactivation of HIF-2a in nearly all clinical cases. In ccRCC, inventors find differential drug sensitivities to drugs such as PD1 and HIF-2α inhibitors.
Further, using immunofluorescent imaging of nuclear speckle protein, SON, inventors demonstrated that SON distribution in the nucleus strongly correlated with ccRCC patient survival. Hence, RNA or imaging methods may be used interchangeably for nuclear speckle assessment.
Advantages:
- Selection marker for ccRCC patients for treatment with HIF2α inhibitors
- Determination of drug sensitivity of ccRCC patients
- Cancer patient outcomes predictions 6 cancer types, particularly in ccRCC
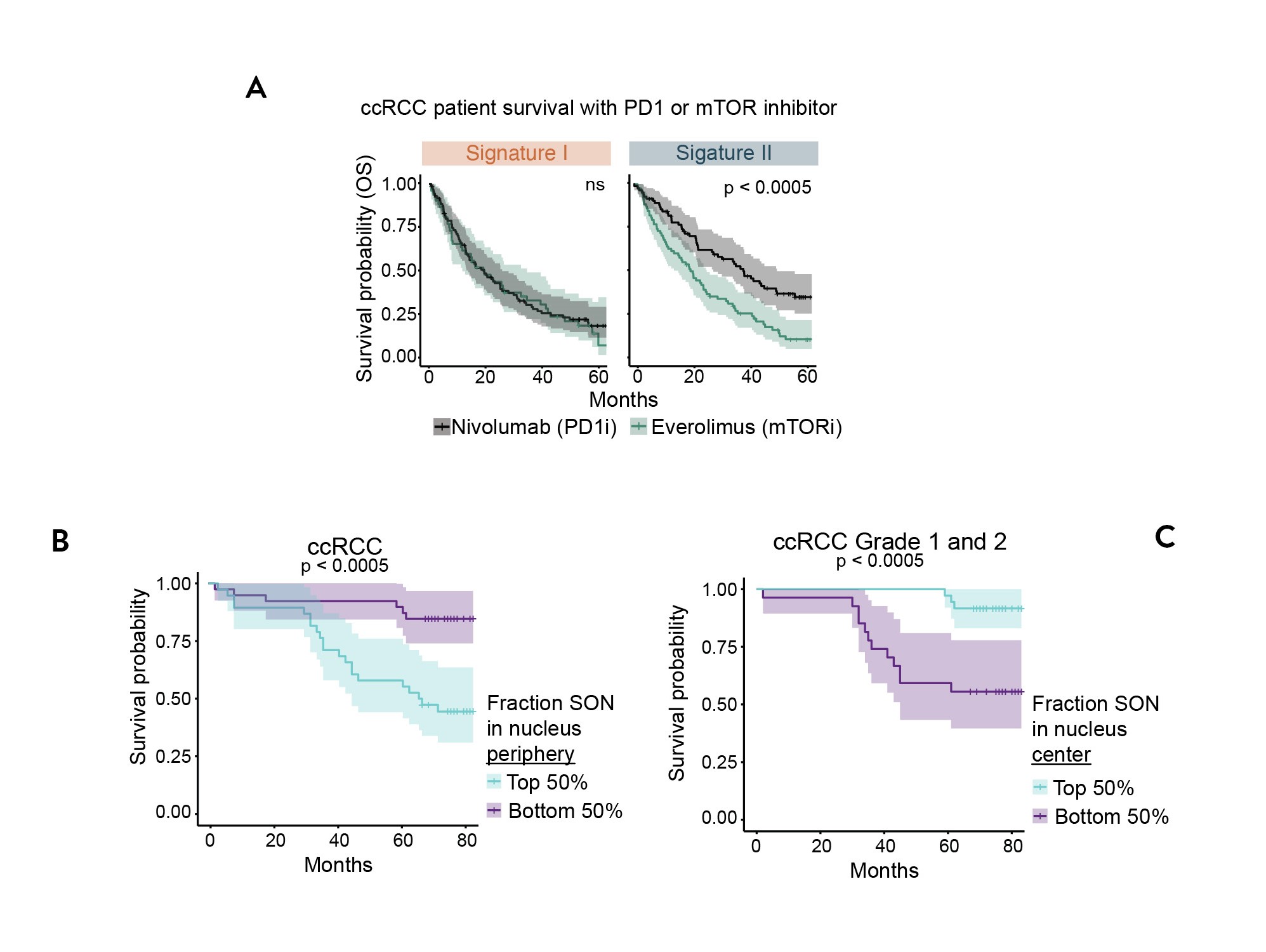
A: ccRCC patient overall survival in response to nivolumab (PD1 inhibitor) or everolimus (mTOR inhibitor) in patients with different RNA-based speckle signatures.
B: Kaplan Meier plot of ccRCC split by SON immunofluorescence pattern in the nucleus
C: Kaplan Meier plot of Grade 1 and 2 ccRCC split by SON immunofluorescence pattern in the nucleus.
Case ID:
22-9922-TpNCS
Web Published:
11/28/2023
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |