AAR-DL (Automatic Anatomy Recognition – Deep Learning) is a hybrid intelligence recognition and delineation segmentation model that outputs automatically delineated organs in medical images by combining natural intelligence’s (i.e., human knowledge’s) and artificial intelligence's strengths to map organs and their boundaries in the given images.
Problem:
Doctors often require organs and anatomical regions of interest to be highlighted in contrast to the background within images from a medical scan. This process is usually done manually by doctors, for whom recognizing the region of interest (ROI) is trivial, but highlighting the accurate boundaries of the part can be very labor-intensive. In contrast, AI models struggle with recognizing the location of an ROI in the image but can quickly delineate the organ of interest from the rest of the image once the ROI is identified. Users are often forced to choose between the opposing approaches without finding a comfortable middle ground.
Solution:
Researchers have now developed a method to combine the ability of humans to recognize the ROI and the accurate delineation abilities of AI to create an automated hybrid intelligence organ recognition and delineation model, mitigating both methods' weaknesses. This process has four steps. First, a computer trims the picture from the medical scan. Then, the computer makes a rough guess about the important part within the picture based on what a knowledgeable human would guess. After that, the computer draws boxes around that area. Finally, the computer makes the selected part look neat and tidy.
Technology:
The model encompasses four distinct phases in image analysis. Initially, the computer system conducts image cropping, denoted as BRR (Body Region Recognition) during the first phase. In the subsequent stage, the system employs a fuzzy recognition approach, named AAR-R (Automatic Anatomy Recognition - Object Recognition), which incorporates human knowledge, to annotate the area of interest. Following this, the system applies a convolutional deep learning network to establish 2D bounding boxes around the identified region, referred to as DL-R (Deep Learning-Based Object Recognition). Lastly, the fuzzy region generated by the preceding phase is precisely delineated with smooth boundaries by an AI system, referred to as DL-D (Deep Learning-Based Object Delineation). When tested on thoracic and head and neck medical images, this approach achieved accuracy at least as good as manual methods for organ segmentation and was more than 70% faster.
Advantages:
- Scores with at least as good accuracy as of clinical manual delineation methods, which represent the reference standard
- 70% faster when compared to the reference standard
- Compatible with large data set analysis in which analysis is time-sensitive
- Avoids the need for AI models to be trained on high-level anatomic data
- High adaptability allows it to find potential utility in all manner of imaging data, including CT, MRI, and PET scans
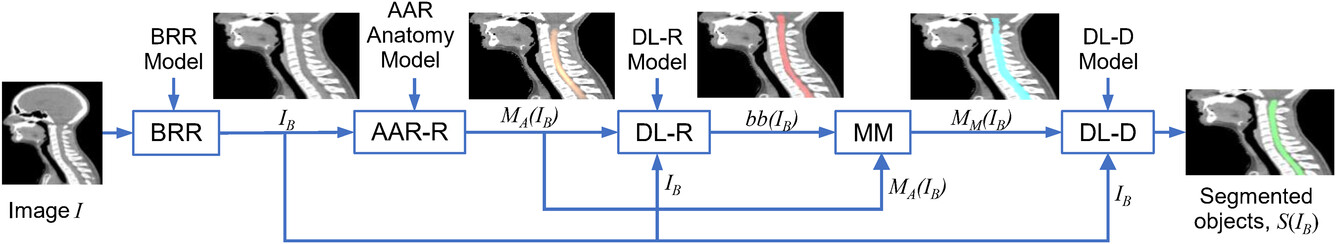
A schematic representation of the different stages (modules) in the proposed hybrid intelligence (HI) system. BRR, body region recognition; AAR‐R, automatic anatomy recognition object recognition; DL‐R, deep‐learning‐based object recognition; MM, model morphing; DL‐D, deep‐learning‐based object delineation.
Case ID:
21-9511-TpNCS
Web Published:
12/21/2023
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |