A radio frequency-based 3D imaging system that can generate LiDAR-comparable images with reduced power and processing needs.
Problem:
With the emergence of robotic and autonomous systems in areas such as transportation, search and rescue, construction, healthcare assistance, and warehouse management, radio frequency (RF) signal-based sensing and imaging is a promising approach generate accurate and robust visualization and object detection of surroundings. RF systems offer distinct advantages over traditional optical sensors as they are resilient against environmental challenges such as dust, fog, and adverse lighting conditions. However, the fundamental limitation of RF sensors lies in their poor resolution. Unlike cameras, RF sensors typically consist of significantly fewer antennas, resulting in limited angular resolution, and smeary or indistinct appearance of objects.
Solution:
PanoRadar - an RF imaging system capable of LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) quality imaging.
Technology:
PanoRadar utilizes a motor-operated, rotating, single-chip millimeter wave (mmWave) radar signal generator coupled with a synthetic array of antennas in a unique cylindrical configuration to generate and capture high resolution images. The dense array and compact wave generation design, coupled with image processing allows for a significantly increased resolution of images.
Advantages:
- Allows for LiDAR quality imaging with RF price points.
- Capable of predicting the surface orientation of objects inside a scene (surface normal estimation).
- Capable of categorizing each pixel in an image into a class or object (semantic segmentation).
- Enables object detection and human recognition.
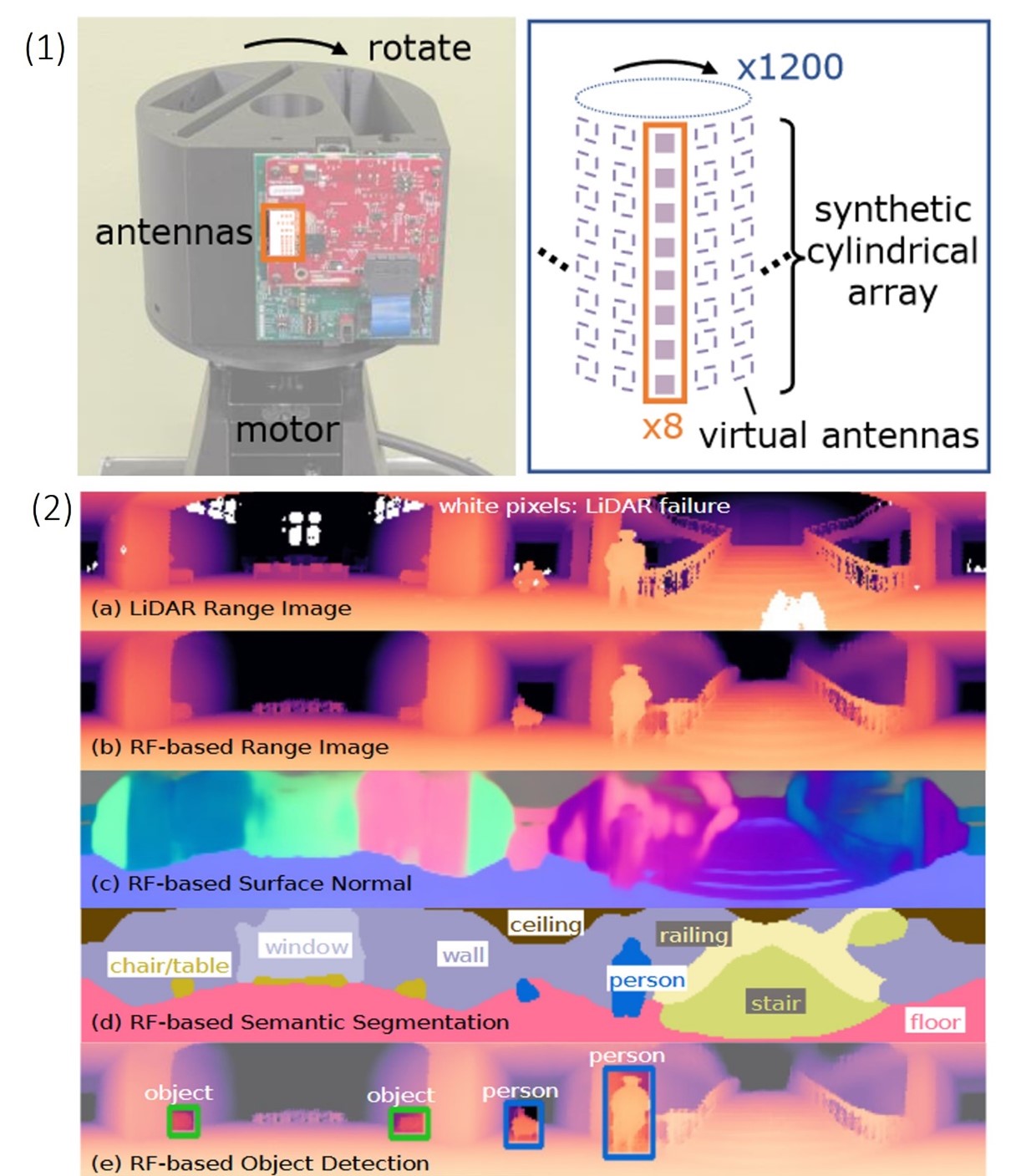
(1) PanoRadar design. Left: The system rotates a single-chip mmWave
radar using a motor. Right: this rotation emulates a dense cylindrical array of antennas. (2) RF imaging and visual recognition with PanoRadar. This figure illustrates the capabilities of the system, showing (a) the 3D panoramic LiDAR range image as a reference, and (b) the RF-based prediction generated by the system. The LiDAR-comparable results enable a variety of visual recognition tasks, including (c) surface normal estimation, (d) semantic segmentation, and (e) object detection and human localization.
Intellectual Property:
- U.S. Patent Application Filed
Case ID:
24-10645-TpNCS
Web Published:
8/23/2024
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |