Pediatric pulmonary artery band (PAB) using origami-inspired fabrication that is remotely adjustable after implantation.
Problem:
Congenital heart defects affect 1% of births in the United States and can lead to irregular blood flow through the main pulmonary artery (MPA). A pulmonary artery band (PAB) is an implant that can be placed on the MPA to restrict blood flow. However, most PAB implants fail to accommodate growth in pediatric patients, which results in frequent reoperation and financial burden. Although remotely controlled PABs have been developed, they are mechanically complex, expensive, and prone to failure.
Solution:
Origami structures were incorporated into the PAB design for easy fabrication, rapid assembly, and multi-state stability. This PAB is minimally invasive and can be periodically adjusted using external magnetic fields to tune blood flow through the MPA.
Technology:
The geometric parameters of a square origami pattern were optimized to enable the origami-inspired PAB (OPAB) device to reconfigure to multiple states. A prototype was laser cut from a sheet of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), manually folded, and assembled using tape. Panels attached to the fold panels enable the OPAB to expand or collapse using external magnetic fields. Mechanical testing indicated that the device’s stability and shape can be predicted when adjusting the device to accommodate for patient growth. During simulated in- vivo testing, the OPAB prototype successfully restricted flow rates in a mock MPA tube.
Advantages:
- Minimally invasive, biocompatible, and compatible with current treatments
- Scalable design and easily fabricated with few constituent parts
- Externally adjustable using magnetic control, reducing the need for surgical reoperations

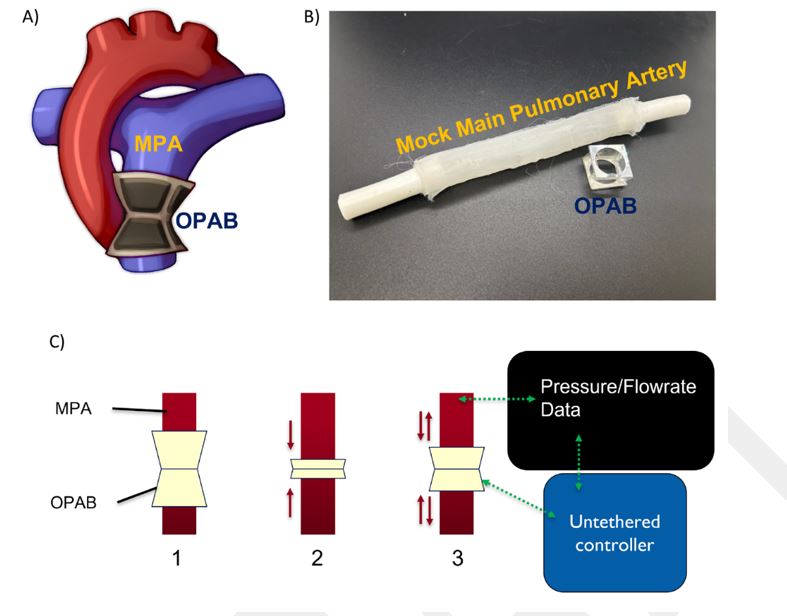
(A) Illustration of the origami-inspired PAB (OPAB; in gray) constricting blood flow through the main pulmonary artery (MPA; in blue) using magnetic panels. (B) The OPAB prototype with tubing represents the MPA. (C) In a clinical setting, a surgeon would 1) place the OPAB around the patient’s MPA, 2) fully compress the OPAB to ensure range of motion, then 3) tune the inner diameter using magnetic fields until blood flow is restricted.
Intellectual Property:
- US Provisional Patent Application Filed
Case ID:
23-10185-01-TpNCS
Web Published:
11/18/2024
Patent Information:
| App Type |
Country |
Serial No. |
Patent No. |
File Date |
Issued Date |
Expire Date |